Question 1
Give three reasons for requirements modelling.
Requirements modeling serves several purposes in the software engineering process:
1. Clarifying Requirements: Modeling helps in clarifying and understanding the
stakeholders' requirements by representing them in a structured and visual format,
which reduces ambiguity and ensures a common understanding among project
team members.
2. Communication: It facilitates communication between stakeholders, developers,
and other project team members by providing a visual representation of the
system's requirements that can be easily understood by all parties involved.
3. Documentation: Requirements models serve as documentation for capturing and
preserving the requirements throughout the software development lifecycle. They
provide a clear record of what needs to be built and why.
4. Analysis: Models enable analysis of the requirements to ensure completeness,
consistency, and feasibility. They allow stakeholders to explore different
scenarios, identify potential conflicts or gaps, and make informed decisions about
the system's design and implementation.
5. Validation and Verification: Requirements models support validation and
verification activities by providing a basis for assessing whether the proposed
solution meets the stakeholders' needs and expectations. They help in detecting
errors, inconsistencies, and omissions early in the development process.
6. Managing Complexity: Modeling helps in managing the complexity of large and
complex systems by breaking down the requirements into smaller, manageable
components and relationships.
Overall, requirements modeling enhances the effectiveness and efficiency of the software
development process by promoting better understanding, communication, analysis, and
management of requirements.
Question 2
Is it possible to begin coding immediately after a requirements model has been created?
While it may be tempting to start coding immediately after creating a requirements
model, it's generally not advisable. Here's why:
1. Incomplete Understanding: Rushing into coding without thorough analysis and
design based on the requirements model can lead to misunderstandings or
misinterpretations of the requirements. This can result in incomplete or incorrect
implementations.
2. Increased Rework: Without a solid understanding of the requirements and a
well-thought-out design, there's a higher likelihood of needing to revisit and
revise the code later. This can lead to increased rework and project delays.
3. Risk of Scope Creep: Starting coding prematurely can make it easier for scope
creep to occur. Additional requirements may surface during the coding process,
leading to frequent changes and disruptions to the development flow.
4. Lack of Alignment: Coding without a clear plan derived from the requirements
model can lead to a lack of alignment between the implemented system and the
stakeholders' expectations. This can result in dissatisfaction and the need for
costly adjustments later.
5. Quality Concerns: Skipping proper analysis and design increases the risk of
introducing errors or bugs into the code. Without adequate planning, the code may
lack modularity, scalability, and maintainability.
Question 3
Describe how the CRC cards can be used to identify classes in requirements analysis.
CRC (Class-Responsibility-Collaboration) cards are a brainstorming tool used in object-
oriented design to identify classes and their relationships during requirements analysis.
Here's how they can be used:
1. Class Identification:
Start by identifying the major concepts, entities, or objects in the problem
domain based on the requirements.
Each major concept becomes a potential class in the system. Write the
name of each class on a separate CRC card.
2. Responsibility Determination:
For each class identified, determine its responsibilities or what it needs to
do to fulfill its role in the system.
Write down the responsibilities of each class on the CRC card. These
responsibilities should be specific actions or behaviors that the class will
perform.
3. Collaboration Analysis:
Identify other classes with which each class interacts or collaborates to
fulfill its responsibilities.
On the CRC card, list the names of other classes with which the class
collaborates. This collaboration could involve passing messages, sharing
data, or invoking methods.
Question 4
There are two different types of “states” that behavioural models can represent. What are they?
- The state of each class as the system performs its function.
- The state of the system as observed from the outside as the system performs its function.
Question 5
How does a sequence diagram differ from a state diagram? How are they similar?
Differences:
Focus: Sequence diagrams focus on interactions between objects over time, while
state diagrams focus on the states and transitions of an object or system.
Representation: Sequence diagrams emphasize message passing and the
chronological order of interactions, whereas state diagrams emphasize the states
and transitions of a system's behavior.
Usage: Sequence diagrams are used to model dynamic behavior and interaction
sequences, while state diagrams are used to model the state-based behavior and
transitions of systems.
Similarities:
Both are graphical models: Both sequence diagrams and state diagrams are
graphical representations used to model aspects of a system's behavior.
Used for analysis and design: Both diagrams are employed during software
analysis and design phases to understand and document system behavior.
Complement each other: While they represent different aspects of behavior,
sequence diagrams and state diagrams can complement each other when modeling
complex systems by providing different perspectives on system behavior.
Question 6
What is the purpose of the interaction model for a Web/Mobile App?
The purpose of the interaction model for a web/mobile app is to outline how users will
interact with the application interface to accomplish their tasks or goals effectively and
intuitively. This model focuses on the user experience (UX) design aspect of the
application and defines how users navigate through the interface, perform actions, and
receive feedback.
Question 7
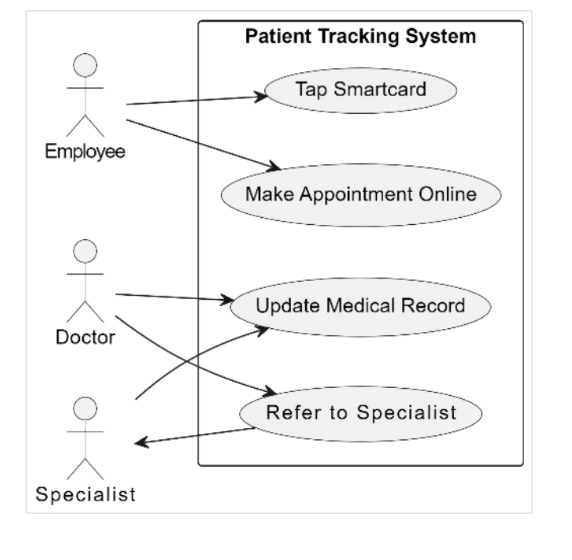
Draw a use case diagram based on the scenario as described below:
XYZ Bhd needs a patient tracking system that tracks each employee's visit to the
company’s clinic. Each employee has an employee ID, name and position. Employees also
have a smartcard which they will have to tap into the system when they want to go to the
company’s clinic to see a doctor. Employees can also make appointments online to reduce
waiting time at the clinic. The doctor adds to the patient’s medical record regarding the
patient's symptoms and treatment and/or medication prescribed. If the case is too
complicated for the staff doctor to handle, the patient would be referred to a specialist at
one of the panel hospitals. This also needs to be recorded in the patient's medical records.
Question 8
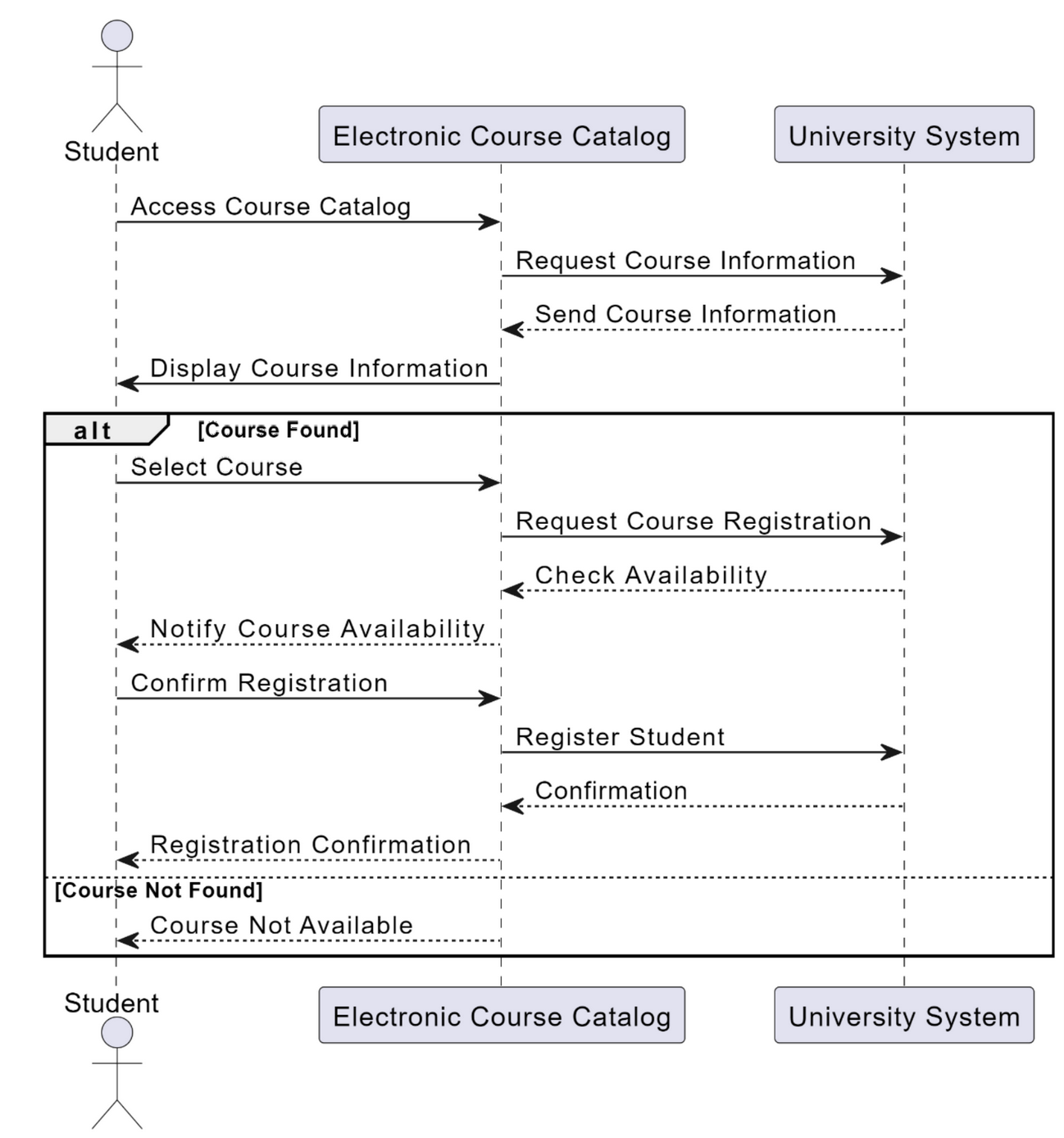
Draw a sequence diagram showing the interactions involved when a student registers for
a course in a university. Courses may have limited enrolment, so the registration process
must include checks that places are available. Assume that the student accesses an
electronic course catalog to find out about available courses.
Question 9
Identify a Web application that you often use. Discuss the following models for the Web application: "Shopee.com"
1. Content Model:
Shopee's content model encompasses a wide range of product listings,
including images, descriptions, prices, ratings, reviews, seller information,
and promotional banners.
Each product page on Shopee provides detailed information about the
item, specifications, availability, shipping options, and seller policies to
help users make informed purchasing decisions.
2. Interaction Model:
The interaction model of Shopee enables users to browse products, search
for items using keywords or filters, add products to the cart, proceed to
checkout, and complete transactions.
It includes interactive elements like buttons, links, search bars, sorting
options, filters, tooltips, and modals to facilitate smooth navigation and
user engagement.
3. Functional Model:
Shopee's functional model includes essential features such as product
search, personalized recommendations, seller ratings, flash sales, chat
support, order tracking, and payment options.
It ensures that the website functions efficiently to handle user interactions,
process orders, manage inventory, handle payments securely, and provide
customer service.
4. Navigation Model:
Shopee's navigation model organizes products into categories and
subcategories, making it easy for users to explore different sections and
find relevant items.
It includes a navigation bar with dropdown menus for browsing
categories, a sidebar for filtering search results, pagination for navigating
through multiple pages of listings, and quick links for accessing popular
sections.
5. Configuration Model:
The configuration model of Shopee allows users to customize their
shopping experience by setting preferences related to language, currency,
location, notification settings, and account preferences.
Users can manage their delivery addresses, payment methods, saved items,
shopping history, and communication preferences to personalize their
interactions with the platform.
Question 10
Identify a mobile application that you often use. Similarly discuss the models for the mobile application: "Tiktok"
1. Content Model:
TikTok's content model primarily consists of short-form videos created
and shared by users. These videos cover a wide range of topics, including
entertainment, humor, dance, challenges, tutorials, and more.
Users can explore a personalized feed of videos based on their interests,
trending topics, hashtags, and accounts they follow. The content model
also includes features such as comments, likes, shares, and user profiles.
2. Interaction Model:
The interaction model of TikTok enables users to scroll through their
video feed, watch videos, interact with content by liking, commenting,
sharing, or saving videos, follow other users, and discover new content
through the "For You" page.
It includes intuitive gestures like swiping up to switch between videos,
tapping to like or comment, holding to record a video, and swiping left or
right to navigate through different sections of the app.
3. Functional Model:
TikTok's functional model includes features like video recording, editing,
filters, effects, duets, challenges, livestreaming, direct messaging,
notifications, user discovery, and profile customization.
It ensures that the app functions smoothly to allow users to create, share,
and consume content seamlessly while providing tools and options to
enhance their videos and engage with the TikTok community.
4. Navigation Model:
TikTok's navigation model is centered around a bottom navigation bar that
provides access to the Home feed, Discover tab, Create video screen,
Inbox for messages, and User profile.
Users can easily switch between tabs to explore different sections of the
app, and additional navigation options are available within each section to
further refine content discovery and interaction.
5. Configuration Model:
The configuration model of TikTok allows users to customize their app
experience by adjusting settings related to privacy, account preferences,
notifications, language, content preferences, and accessibility options.
Users can manage their profile settings, privacy settings, blocking and
reporting preferences, notification settings, and preferences for
personalized recommendations to tailor their TikTok experience to their
preferences.

